SQL Lesson 17 - Altering tables
As your data changes over time, SQL provides a way for you to update your corresponding tables and database schemas by using the ALTER TABLE statement to add, remove, or modify columns and table constraints.
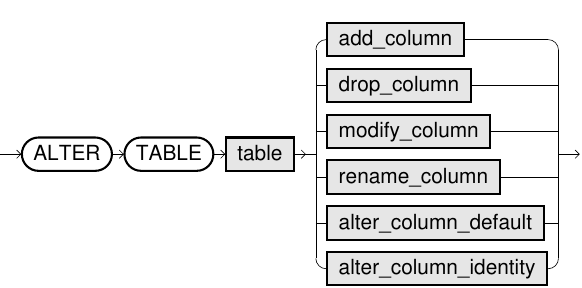
Adding columns
The syntax for adding a new column is similar to the syntax when creating new rows in the CREATE TABLE statement. You need to specify the data type of the column along with any potential table constraints and default values to be applied to both existing and new rows. In some databases like MySQL, you can even specify where to insert the new column using the FIRST or AFTER clauses, though this is not a standard feature.
Altering table to add new column(s)
ALTER TABLE mytable ADD column _DataType_ _OptionalTableConstraint_ DEFAULT default_value;
Removing columns
Dropping columns is as easy as specifying the column to drop, however, some databases (including SQLite) don't support this feature. Instead you may have to create a new table and migrate the data over.
Altering table to remove column(s)
ALTER TABLE mytable DROP column_to_be_deleted;
Renaming the table
If you need to rename the table itself, you can also do that using the RENAME TO clause of the statement.
Altering table name
ALTER TABLE mytable RENAME TO new_table_name;
Other changes
Each database implementation supports different methods of altering their tables, so it's always best to consult your database docs before proceeding: MySQL, Postgres, SQLite, Microsoft SQL Server.
Exercise
Our exercises use an implementation that only support adding new columns, so give that a try below.
1. Add a column named **Aspect_ratio** with a **FLOAT** data type to store the aspect-ratio each movie was released in.
1. ALTER TABLE movies ADD Aspect_ratio FLOAT;
2. Add another column named **Language** with a **TEXT** data type to store the language that the movie was released in. Ensure that the default for this language is **English**.
1. ALTER TABLE movies ADD Language TEXT DEFAULT 'English';
Exercise 17 — Tasks
1. Add a column named **Aspect_ratio** with a **FLOAT** data type to store the aspect-ratio each movie was released in. ✓
2. Add another column named **Language** with a **TEXT** data type to store the language that the movie was released in. Ensure that the default for this language is **English**. ✓
Here’s a summary of the current SQLBolt lesson on altering tables:
- The lesson explains how to use the SQL
ALTER TABLEstatement to update tables and schemas as your data needs change. - You can use
ALTER TABLEto:- Add new columns: Specify the new column's data type, constraints, and default values. Some databases (like MySQL) allow you to choose where to insert the column, though this is not standard.
- Remove columns: Remove a column by specifying its name. However, not all databases (e.g., SQLite) support this directly—you might have to create a new table and migrate data instead.
- Rename tables: Change the table name using the
RENAME TOclause.
- Each SQL database (MySQL, Postgres, SQLite, SQL Server) may have differences in how
ALTER TABLEworks, so it’s important to check database-specific documentation. - The exercise in this lesson only supports adding new columns to practice.
The page also includes an example movie table and asks you to add columns for "Aspect_ratio" (FLOAT) and "Language" (TEXT, default "English") as part of the exercises.[1]
Here are concise examples of ALTER TABLE usage across different SQL environments:
1. Add Column
- Standard SQL/MySQL/PostgreSQL:
ALTER TABLE users ADD email VARCHAR(255); - MySQL (specify position):
ALTER TABLE users ADD age INT AFTER name;
2. Drop Column
- MySQL/PostgreSQL/SQL Server:
ALTER TABLE users DROP COLUMN age; - SQLite (not supported directly; requires creating new table and migrating data)
3. Modify Column
- MySQL:
ALTER TABLE users MODIFY email VARCHAR(512); - SQL Server:
ALTER TABLE users ALTER COLUMN email NVARCHAR(512); - PostgreSQL:
ALTER TABLE users ALTER COLUMN email TYPE VARCHAR(512);
4. Rename Column
- MySQL:
ALTER TABLE users CHANGE old_email new_email VARCHAR(255); - PostgreSQL/SQLite:
ALTER TABLE users RENAME COLUMN old_email TO new_email;
5. Rename Table
- All major SQL environments:
ALTER TABLE users RENAME TO customers;
6. Add/Drop Constraints
- MySQL/PostgreSQL:
ALTER TABLE users ADD CONSTRAINT unique_email UNIQUE (email); ALTER TABLE users DROP CONSTRAINT unique_email;
Note: Feature support and syntax details may vary between databases—always refer to relevant documentation.